Deleting Node to Which Nodeptr Points Using Smart Pointer C
Your function must follow following constraints. C a pointer to C Output.

C How To Correctly Dereference A Void Pointer To Class Stack Overflow
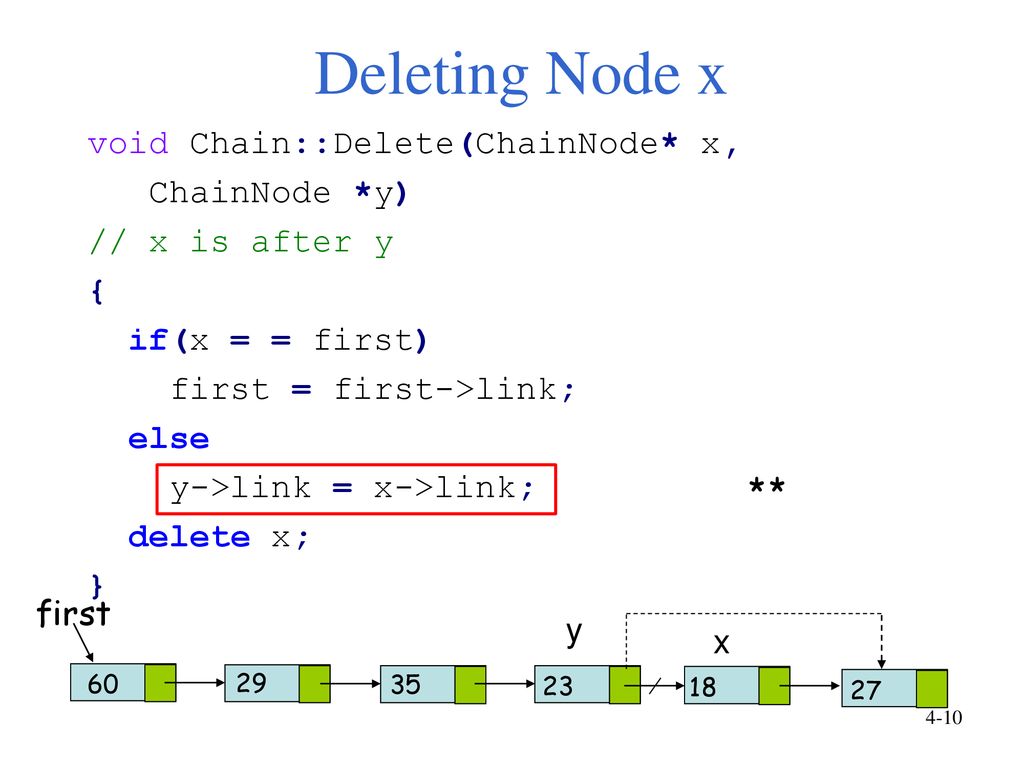
Copy data of next node to this node node_ptr-data temp-data.
. For example if we have a linked list a b c then to delete the node b we will connect a to c ie a c. Void somefunc1 creating a new dummy node node NodeDummycreate. Deleting the node nodedeleteLater.
For a Slice class the compiler generates a C smart pointer called PtrRather than showing all the details of the generated class here is the basic usage pattern. Pointing temp to link part of current node ie. Remove_all We may also be interested to remove all nodes from a linked list whose data is equal to some specified integer value.
You create the object and then let the system take care of deleting it at the correct time. Link-based Implementation of the ADT Binary Search Tree. A Smart Pointer is a wrapper class over a pointer with an operator like and - overloaded.
2 It should not return a pointer to the head node. Drop ----. When the object is destroyed it frees the memory as well.
Get the data of next node Node-iData temp-iData. Declare temp to store node values 2. Get the Address of next.
You can transfer the contents of one Shared Pointer to another leaving the original Shared Pointer empty with the MoveTemp or MoveTempIfPossible function. Get the Address of the next node NodePointer temp Node-pNextNode. Given a Singly Linked List write a function to delete a given node.
So we dont need to delete it as Smart Pointer does will handle it. Remove_nodehead n Removig all nodes satisfying a condition from a linked list. When found removes and deletes the node ----- bool LListdropint k node currentNode searchk.
The pointer in a node points to Select one. NodePtr n search_nodehead value. C11 comes up with its own mechanism thats Smart Pointer.
Access the encapsulated pointer by using the familiar pointer operators - and which the smart pointer class overloads to return the encapsulated raw pointer. Next node temp ptr - link. We do this cleaning by the use of delete operator.
If currentNode NULL removecurrentNode return false. Smart pointers are generated by the Slice compiler for each class type. Create a temporary pointer to the node B.
Void somefunc2 checking whether the node exists if node LogmessageThe node is aliven. For a Slice class the compiler generates a C smart pointer called PtrRather than showing all the details of the generated class here is the basic usage pattern. The count part of a node.
Copy data and link part of next node to current node ptr - data temp - data. Node tmp currentNode. Whenever you allocate a class instance on the heap you simply assign the pointer returned from new to a.
The C smart pointer idiom resembles object creation in languages such as C. Source Code - C void deleteNode Node ptr creating temporary pointer Node temp. Move the contents of PointerOne over to PointerTwo.
Smart pointer is a wrapper class over a pointer with operator like and - overloaded. Note that before C11 C did have one smart pointer class auto_ptrThis was unsafe and is now deprecated with unique_ptr replacing it. Go to the next node nodenode-next.
If you are not familiar with the delete operator then you can visit the Dynamic memory chapter of the C course. The pointer part of the node. We delete any node of a linked list by connecting the predecessor node of the node to be deleted by the successor node of the same node.
Unlink next node node_ptr-next temp-next. Struct Node int data. The objects of smart pointer class look like pointer but can do many things that a normal pointer cant like automatic destruction yes we dont have to explicitly use delete reference counting.
While node-next swap value only with the next node temp node-data. While tmp NULL currentNode currentNode-dup. The objects of the smart pointer class look like normal pointers.
The fast solution is to copy the data from the next node to the node to be deleted and delete the next node. The fast solution is to copy the data from the next node to the node to be deleted and delete the next node. This can easily be done using a loop and the search_node and remove_node functions as follows.
Smart pointers are generated by the Slice compiler for each class type. Something like the following. To use these classes youll need to.
Delete current node free temp. Point current node to link part of next node ptr - link temp - link. Defination of each node is as follows.
Find next node using next pointer struct Node temp node_ptr-next. Searches for a node in the list with the given key. There is no practical solution to delete a node directly by given pointer we need to do some trick.
NodeToConnectPtr nodePtr-getRightChildPtr Delete the node to which nodePtr points done for us if nodePtr is a smart pointer returnnodeToConnectPtr else N has two children. The data part of a node. Whenever you allocate a class instance on the heap you simply assign the pointer returned from new to a.
Headitem is the same as. But this will make the node b inaccessible and this type of inaccessible nodes are called garbage and we need to. Delete next node free temp.
A a pointer to A Output. Removing data from a stack is called popping the stack. One big change to modern C style that comes with C11 is that you should never need to manually delete or free anymore thanks to the new classes shared_ptr unique_ptr and weak_ptr.
Using smart pointers we can make pointers to work in way that we dont need to explicitly call delete. 1 It must accept a pointer to the start node as the first parameter and node to be deleted as the second parameter ie a pointer to head node is not global. B--D--E--F It would be a simple deletion problem from the singly linked list if the head pointer was given because for deletion you must know the previous node and you can easily reach there by.
Both PointerOne and PointerTwo now reference nullptr. IfC is a left child nodeToConnectPtr nodePtr-getLeftChildPtr else. Declare ListNode pre and initialize to address of node to be deleted.
A simple solution is to traverse the linked list until you find the node you want to deleteBut this solution requires a pointer to the head node which contradicts the problem statement. We need to copy the data from the next node to the current node by given pointer to be deleted and delete the next node. So the steps to be followed for deletion of the node B from the linked list A B C are as follows.

Ic210 Pointer Basics Linked Lists Intro

Linked List Implementation In C Techie Delight
Data Structures Chapter 4 Linked Lists Ppt Download

Delete All Odd Nodes Of A Circular Linked List Geeksforgeeks
C Smart Pointer Learning And Use
C Smart Pointer Learning And Use
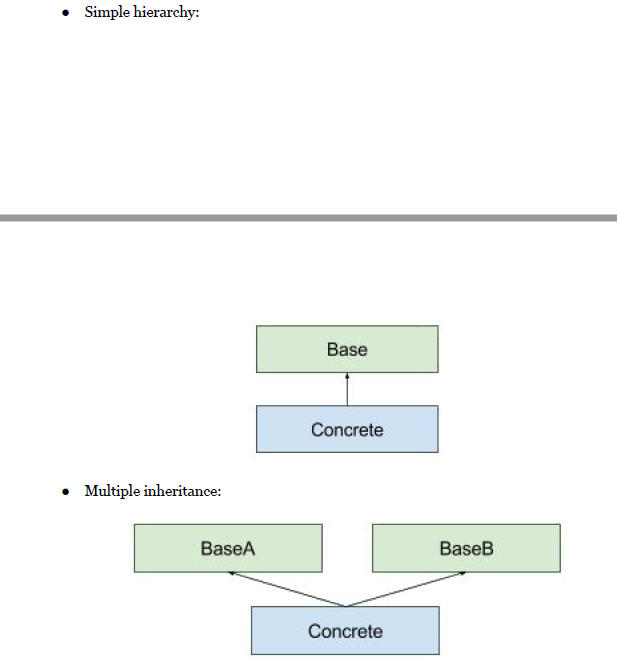
C Smart Pointer Learning And Use
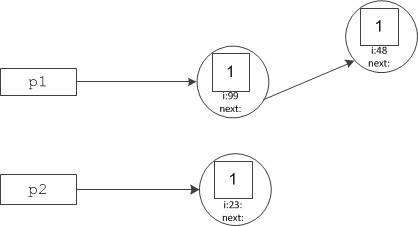
Smart Pointers For Classes Ice

C Segmentation Fault In Recursive Function When Using Smart Pointers Stack Overflow

Data Structures Chapter 4 Linked Lists Ppt Download
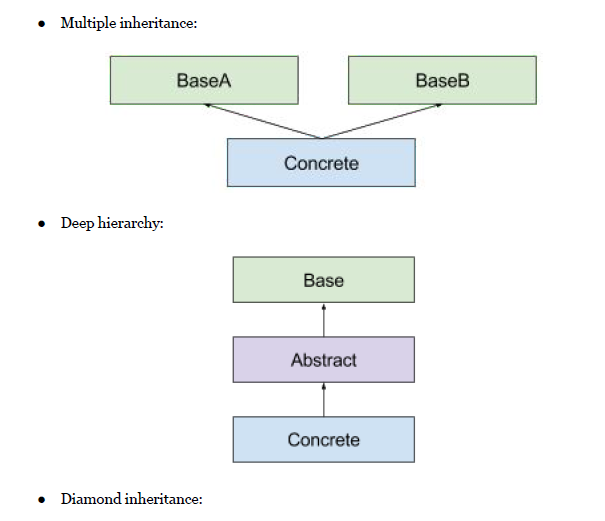
C Smart Pointer Learning And Use

C Smart Pointer Learning And Use
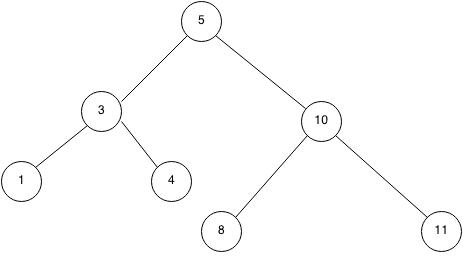
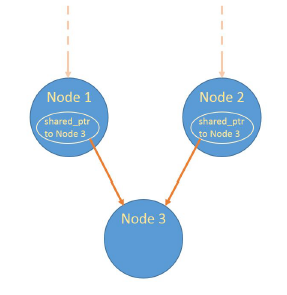
C 11 Smart Pointer Part 5 Shared Ptr Binary Trees And The Problem Of Cyclic References Thispointer
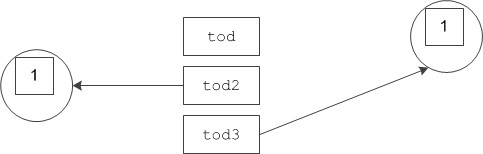
Smart Pointers For Classes Ice

C Segmentation Fault In Recursive Function When Using Smart Pointers Stack Overflow
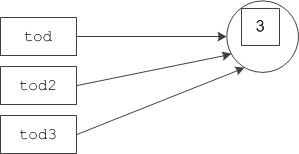
Comments
Post a Comment